What is RIS?
The concept behind RIS (Railway Infrastructure System) is to merge several existing systems that contain parts of the digital infrastructure data such as CRD (Central Reference Files Database), Geo Editor, CIP (Customer Information Platform) and RFP (Rail Facilities Portal), along the use of RINF (Register of Infrastructure) as a source for railway infrastructure data. The new RNE Railway Infrastructure System will build up the work initiated in 2017 with the Big Data Framework.
RIS aims to create a single digital infrastructure system capable of serving all railway actors by providing different data representation based on their business needs. This system is envisioned to be a central place for digital railway infrastructure data within the Railway Sector and act as a cornerstone of multitude other systems within the Railway Sector, especially sales, capacity planning and operations.
Goals of RIS
- To integrate several existing systems: this system should replace several existing systems by merging their data and functions into one consistent entity.
- To reduce operational and management costs by providing greater added value to the end-users.
- To be designed and built using state-of-the-art technologies to ensure stable operation in the following 3-5 years without a risk of technological deprecation.
- To ensure higher level of cybersecurity than the existing ones.
Also, the new system must comply with the same legal requirements that are currently met by the RNE systems that will be replaced.
Benefits of RIS
- Shared data
By connecting the data from current isolated systems, we increase the functionality of each of them and the systems that use their data.
- Shared system infrastructure
By merging different systems in one (larger) system, their dedicated resources will be reduced, lowering the operating and managing costs.
- Common functions and process
In every system, there are several common functions that are necessary but do not add business value to the system.
- Data Granularity
The system aims to offer digital railway infrastructure data at both macro and meso levels to other systems based on their requirements.
- Time dimension
Time dimension refers to the possibility of using the data as it was or as it will be in a specific time. This is achieved by providing a validity period to each element of the data model.
Current and future state of Big Data
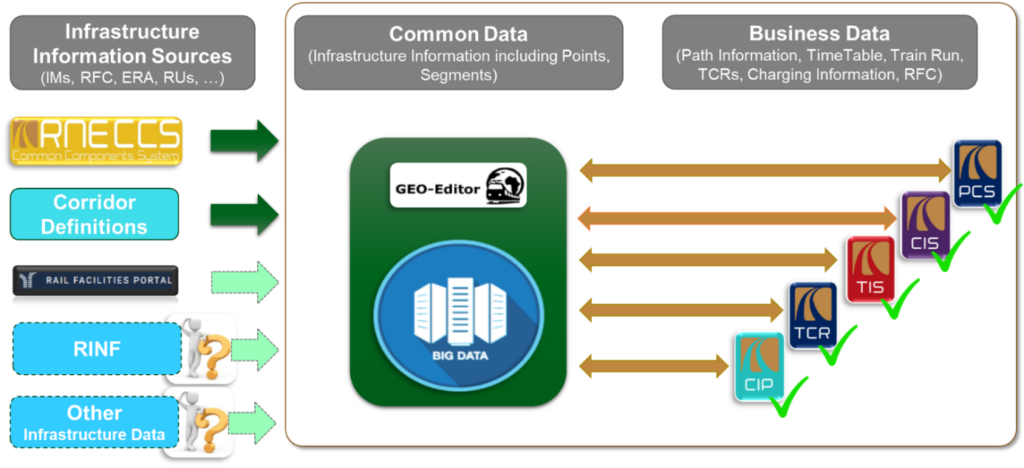
The new RNE Railway Infrastructure System will continue the work started in 2017 with the Big Data Framework. Since RNE business applications are already using the same infrastructure information, the next step is to create a single access point for the data, including Rail Freight Corridor and Railway Service Facilities information that are currently isolated.
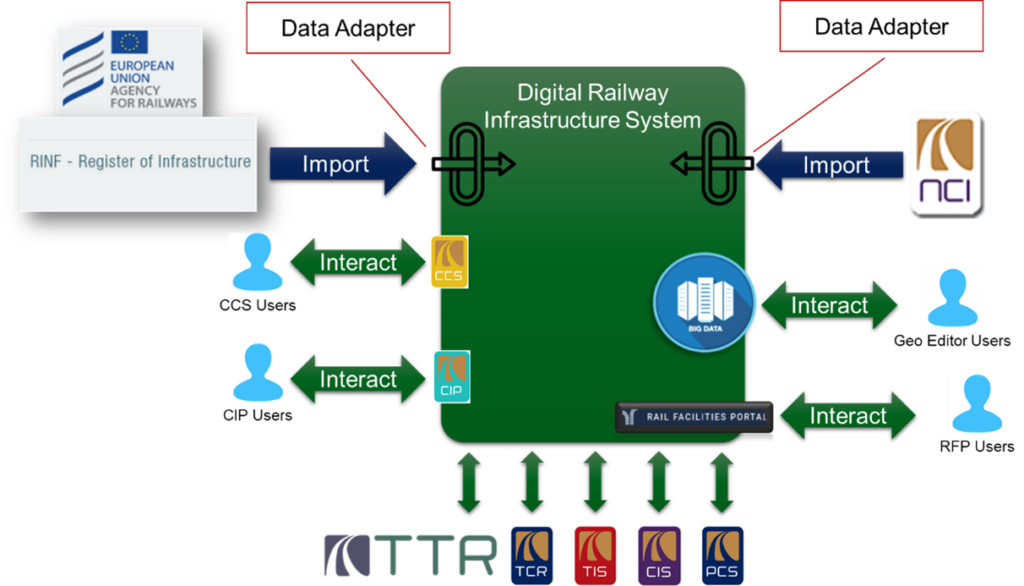
By combining existing systems into a new system, along with exchanging data with RINF and other sector systems, it will lead to enhancement of services provided by RNE business applications or any other systems seeking a centralised and comprehensive description of the European railway network.